Alignments¶
Click Alignments in the top navigation bar to enter the alignment module, where you can perform best fit alignment,
transform alignment,
local alignment,
matrix alignment and
RPS alignment.
Note
- For a measured model, multiple alignment methods can be used to calculate multiple alignment results. However, in the current model preview scene, only one alignment result can be displayed (right-click and Activate the alignment object in the left-side tree view) to determine the current pose of the measured model. Inactive alignment objects can be deleted by right-clicking on them.
- You can right-click on an alignment object in the left-side tree view and click Export Matrix to save the matrix file (*.txt) of that object locally. This file can be used for matrix alignment.
Best Fit Alignment¶
Through the best fit alignment, you can align the measured model automatically by moving its pose based on the reference model, minimizing the overall average distance deviation.
Note
Before using the best fit alignment function, please import the reference model and the measured model.
The steps for performing the best fit alignment are as follows:
Col
- In the Alignment Tools bar, click
Best Fit Alignment to open the corresponding window.
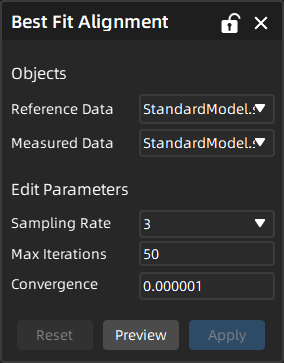
- Select the reference data and measured data to be aligned, and edit the parameters (sampling rate, maximum iterations and convergence).
- Click Preview to preview the alignment result in the 3D scene; then click Apply to save the alignment object, which will be displayed in the align group corresponding to the measured model in the left-side tree view.
- (Optional) Right-click on the best fit alignment object in the left-side tree view to edit the alignment and trigger the recalculation function.
Col
Transform Alignment¶
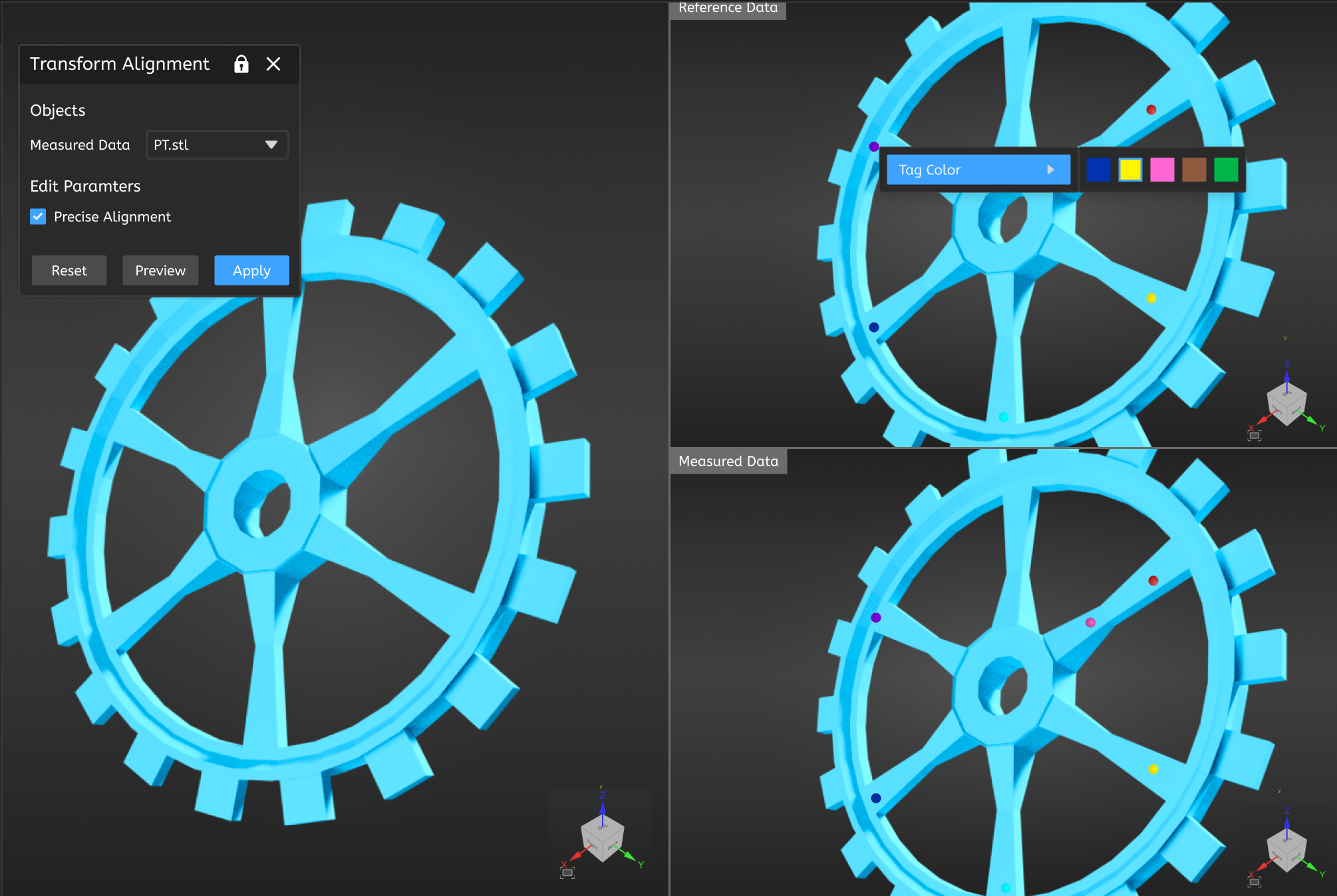
In cases where the best fit alignment function cannot be used for automatic model alignment, you can use the transformation alignment function to manually align the reference and measured models by selecting at least three (up to six) sets of points on them.
Note
Before using the transform alignment function, please import the reference model and the measured model.
The steps for performing the transform alignment are as follows:
Col
- In the Alignment Tools bar, click
Transform Alignment to open the corresponding window.
- Select the measured data to be aligned, and select at least three (up to six) sets of points on models in the Reference Data and Measured Data window respectively:
- Drag the points to change their positions.
- Right-click on a point to change the tag color of that point.
- Press Del after selecting a point to delete it.
- Click Preview to preview the alignment result in the 3D scene; then click Apply to save the alignment object, which will be displayed in the align group corresponding to the measured model in the left-side tree view.
Col
Local Alignment¶
In cases where the best fit alignment result does not meet the actual requirements, you can use the local alignment function to fine-tune the alignment by selecting faces on the reference model, aiming to minimize the average distance deviation of the selected faces.
Caution
Before using the local alignment function, it is recommended that you first use the best fit or matrix alignment function to ensure that the measured model is in a similar pose to the reference model. Otherwise, it may result in the failure of local alignment.
The steps for performing the local alignment are as follows:
Col
- In the Alignment Tools bar, click
Local Alignment to open the corresponding window.
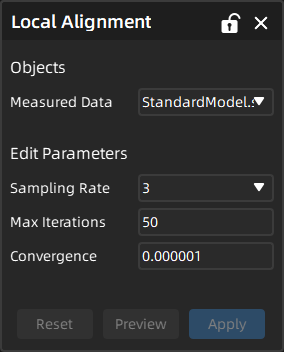
- Select the measured data to be aligned, edit the parameters (sampling rata, max iterations, convergence), and select faces on the reference mode.
- Click Preview to preview the alignment result in the 3D scene; then click Apply to save the alignment object, which will be displayed in the align group corresponding to the measured model in the left-side tree view.
Col
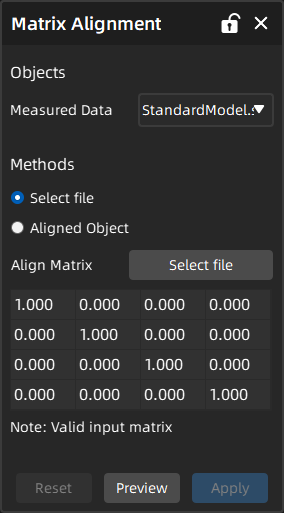
Matrix Alignment¶
Through the matrix alignment, you can directly move the pose of the measured model and automatically align it based on an existing matrix file (TXT or TRM) or the matrix of an alignment object.
Note
Before using the matrix alignment function, please import the measured model.
The steps for performing the matrix alignment are as follows:
Col
- In the Alignment Tools bar, click
Matrix Alignment to open the corresponding window.
- Select the measured data to be aligned and select an alignment method (select a file or an aligned object).
- Click Apply to save the alignment object, which will be displayed in the align group corresponding to the measured model in the left-side tree view.
- (Optional) Right-click on the matrix alignment object in the left-side tree view to edit the alignment and trigger the recalculation function.
Col
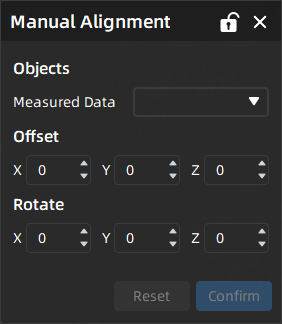
Manual Alignment¶
In cases where there are noticeable differences between the pose of the measured model and the reference model, manual alignment can be used to make fine adjustments to the initial position of the measured model.
Note
Before using the manual alignment function, please import the measured model.
The steps for performing the manual alignment are as follows:
Col
- In the Alignment Tools bar, click
Manual Alignment to open the corresponding window.
- Select the measured data to be aligned, and edit the pan distance or rotation angle of the model on the X / Y / Z axes; you can also manually drag or rotate the movable coordinate axes at the center of the model in the 3D scene.
- Click Confirm to save the alignment object, which will be displayed in the align group corresponding to the measured model in the left-side tree view.
Col
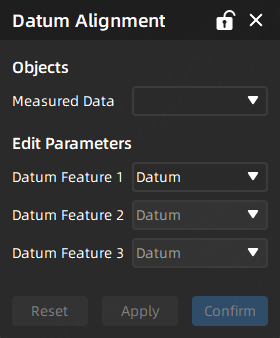
Datum Alignment¶
For workpieces that already have a datum system, existing datum can be used for datum alignment.
Note
- Before using the datum alignment function, please import the measured model, and ensure that there are at least three pairs of datums containing both reference feature and measured feature.
- Before using the datum alignment function, it is recommended that you perform best fit alignment first to automatically align the model preliminarily.
Caution
If it prompts that " Calculation failed, please reselect the datum", please check if the selected three datums can constrain all degrees of freedom of the model in the X / Y / Z axes; if it still fails, please contact technical support.
The steps for performing the datum alignment are as follows:
Col
- In the Alignment Tools bar, click
Datum Alignment to open the corresponding window.
-
Select the measured data to be aligned, and select the datum features (including points, lines, planes, spheres, cylinder axes and cone axes) one by one.
Note
If the datum feature 2 or 3 is selected, readjusting the datum feature 1 will automatically clear the selection of other datums.
-
Click Preview to preview the alignment result in the 3D scene; then click Confirm to save the alignment object, which will be displayed in the align group corresponding to the measured model in the left-side tree view.
Col
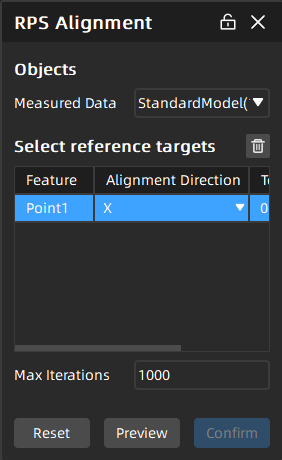
RPS Alignment¶
By using RPS (Reference Point System) alignment, the specified points, circle, and sphere features can be matched to align the models. This method is mainly applied in scenarios such as workpiece alignment, assembly parts, quality control, reverse engineering, and multi-point measurement.
Note
- Before using the RPS alignment function, please import the reference model and measured model, and ensure that there are at least three feature pairs that contain both reference and measured features.
- If you select an existing circle or sphere feature, the corresponding center of the circle or sphere will be taken as the reference point.
- It is recommended that you use point features created with the CMM method as reference points to achieve the best alignment results.
The steps for performing the rps alignment are as follows:
Col
- In the Alignment Tools bar, click
RPS Alignment to open the corresponding window.
-
Select the measured data to be aligned, and click in the 3D scene to select at least three feature pairs or labels, and the selected features will be shown in the Select reference targets column.
Note
- Please select point, circle or sphere features, or it will prompt that "
This feature type is not supported".
- Please select feature pairs that contain both reference and measured features, or it will prompt that "
The select feature pair needs to contain both reference and measured features".
- Please select point, circle or sphere features, or it will prompt that "
-
In the RPS Alignment window, select the Alignment Direction and edit parameters (tol, weight, max iterations, etc.).
Note
By default, the X, Y, and Z directions are
 checked simultaneously; you can click to uncheck them, but at least one direction must be selected.
checked simultaneously; you can click to uncheck them, but at least one direction must be selected. -
Click Preview to preview the alignment result in the 3D scene; then click Confirm to save the alignment object, which will be displayed in the align group corresponding to the measured model in the left-side tree view.
Col